Introduction to Processes
Marketing Processes are an essential component of any commercial enterprise that seeks to create, talk, deliver, and alternate prices to its clients. It involves diverse methods designed to identify, appeal to, and keep customers while at the same time attaining the company’s dreams. These processes are crucial for businesses to understand their target audience, build strong relationships, and drive revenue.
Here are some key processes in marketing:
1. Market Research
Market studies are the muse of all marketing sports. It entails accumulating and reading the target market’s records, including customer wishes, preferences, behaviors, and competitors. By gaining expertise in the market, groups can make knowledgeable selections and broaden effective advertising techniques. By understanding the market, businesses can make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies.
2. Segmentation and Targeting
Once the market studies are carried out, the next step is to section the market based totally on factors such as demographics, psychographics, and conduct. This process allows businesses to divide the market into distinct groups with similar characteristics. After segmentation, the enterprise identifies its target marketplace, and the precise institution(s) it aims to serve with its products or services.
3. Product/Service Development
The technique of making or improving products and services that meet the needs and alternatives of the target market. It includes designing, checking out, and refining the services to make certain they provide value and cope with customer pain factors.
4. Branding and Positioning
Branding is the technique of making a unique and recognizable identification for the business or its products or offerings. Positioning, then again, entails organizing a specific area inside the minds of the customers relative to the competition. Effective branding and positioning help build customer loyalty and preference.
5. Promotion and Advertising
Promotion is the verbal exchange of the services or products’ blessings and capabilities with the target market. Advertising is one of the most commonplace promotion strategies, involving the use of various channels such as TV, radio, print, virtual, and social media. Other promotional activities encompass public relations, sales promotions, and direct advertising and marketing.
6. Distribution and Channel Management
Distribution refers to the technique of turning in services or products from the producer to the give-up customer. Channel management entails selecting and managing the maximum number of green distribution channels, inclusive of wholesalers, retailers, and online platforms, to reach the target market effectively.
7. Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Sales are the process of converting leads into paying customers. An efficient sales process involves prospecting, lead qualification, pitching, negotiating, and closing the sale. CRM encompasses managing interactions with customers throughout their lifecycle to foster long-term relationships and repeat business.
8. Digital Marketing and Analytics
In the digital age, online marketing performs a big function. Digital advertising and marketing encompass numerous channels, along with websites, social media, electronic mail, engines like Google, and content advertising. Analytics equipment is used to track and measure advertising performance, presenting valuable insights to optimize strategies.
9. Evaluation and Improvement
Continuous evaluation of marketing efforts is essential to gauge the effectiveness of various activities. Metrics consisting of return on investments (ROI), customer satisfaction, and purchaser retention prices help groups discover areas for development and refine their advertising process.
In conclusion, marketing procedures are essential for companies to apprehend their target marketplace, expand products and offerings that meet consumer wishes, and effectively promote and distribute them to achieve business goals. By following nicely defined methods, companies can construct robust brand focus, and consumer loyalty, and ultimately drive boom and success.
Definitions of Processes
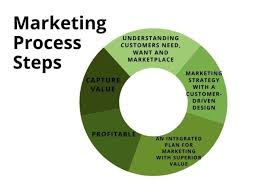
The marketing process is the series of steps businesses follow to promote their products or services to potential customers. It involves identifying the target audience, creating a marketing strategy, implementing the plan, and capturing customer value.
The Marketing Process is a step-by-step method that enables businesses to reach their target audience effectively. It involves understanding market needs, developing a customer-centric strategy, delivering and promoting products or services, and continuously evaluating performance for optimization.
The marketing process refers to the series of steps that assist businesses in planning, analyzing, implementing, and adjusting their marketing strategy.
Features of Processes
1. Systematic Approach
Marketing processes are organized and follow a structured approach. They involve a series of sequential steps or activities designed to achieve specific marketing objectives. A systematic approach ensures that marketing efforts are well-coordinated and result-oriented.
2. Goal-Oriented
Each marketing process is aligned with specific goals and objectives. Whether it’s increasing brand awareness, generating leads, driving sales, or enhancing customer loyalty, marketing processes are designed to achieve measurable outcomes.
3. Customer-Centric
Successful marketing processes focus on understanding and meeting customer needs. Market research, segmentation, and customer relationship management are all centered around providing value to customers and building strong relationships.
4. Data-Driven
The marketing process relies on data and insights to make informed decisions. Data analysis helps identify market trends, customer preferences, and the effectiveness of marketing strategies, allowing for continuous improvement.
5. Iterative and Continuous
The marketing process is not static but rather iterative and continuous. Businesses regularly evaluate and refine their marketing efforts based on feedback and results. This ongoing improvement helps adapt to changing market dynamics and customer behavior.
6. Multichannel Integration
The marketing process often involves multiple channels and platforms to reach the target audience effectively. The integration of diverse advertising and marketing channels, including traditional advertising, virtual advertising, and social media, ensures a complete and cohesive advertising technique.
7. Collaborative Efforts
Marketing tactics regularly require collaboration among one-of-a-kind teams in the company, which includes marketing, income, product improvement, and customer service. Effective verbal exchange and coordination among these groups are critical for successful advertising campaigns.
8. Measurable Metrics
The marketing process uses key overall performance indicators (KPIs) and different metrics to degree fulfillment and tune development in the direction of advertising and marketing goals. Metrics like return on investment (ROI), conversion costs, client acquisition prices, and client lifetime prices provide precious insights for selection-making.
9. Adaptability
Marketing procedures want to be adaptable to changes in the market, customer choices, and rising technology. Flexibility lets businesses respond quickly to new opportunities and challenges.
10. Customer Experience Focus
The marketing process emphasizes delivering a positive customer experience. From the initial interaction with the brand to post-purchase support, providing a seamless and enjoyable customer journey is vital for building loyalty and advocacy.
11. Compliance and Ethics
The marketing process adheres to ethical standards and legal regulations. Businesses ensure their advertising practices are obvious, honest, and respectful of consumer privacy.
In the end, marketing approaches play a vital role in attaining advertising targets, building brand value, and fostering client relationships. They are dynamic, customer-centric, statistics-driven, and constantly evolving to meet the changing needs of the marketplace and customer expectations.

Importance of Processes
Processes play a crucial role in marketing by providing structure, consistency, and efficiency to various activities and strategies. Here are some key reasons why processes are important in marketing:
1. Consistency
The marketing process helps ensure that the messaging, branding, and overall customer experience remain consistent across different channels and interactions. This consistency builds trust and recognition among customers, making your brand more memorable and reliable.
2. Efficiency
Well-defined marketing process streamline workflows and eliminate redundancies. This results in time and useful resource savings, permitting your advertising and marketing crew to focus on strategic sports and creative endeavors instead of getting bogged down with repetitive obligations.
3. Scalability
As your business grows, it becomes increasingly important to have a scalable advertising process in your region. With clearly documented process, it’s easier to onboard new team members, delegate tasks, and expand marketing efforts without losing quality.
4. Measurable Results
Processes allow you to set clear goals, track progress, and measure the effectiveness of your advertising campaigns. By following a structured approach, you could examine statistics and make information-driven selections to refine your techniques and obtain higher effects over time.
5. Adaptation and Improvement
Marketing strategies aren’t set in stone; they may be adjusted and advanced based totally on converting marketplace traits, purchaser choices, and technological advancements. Regularly reviewing and updating process allows you to stay relevant and responsive to the evolving landscape.
6. Risk Management
Documented process provide a framework for handling various scenarios, mitigating risks, and ensuring compliance with regulations. This is particularly important in areas like data privacy, advertising standards, and customer communication.
7. Cross-Functional Collaboration
Marketing often involves collaboration with other departments, such as sales, product development, and customer support. Well-defined process facilitate communication and coordination between these departments, leading to better alignment and smoother execution of joint initiatives.
8. Customer Experience
The marketing process can include customer journey mapping, which helps identify touchpoints where customers interact with your brand. By optimizing these touchpoints, you can enhance the overall customer experience and increase customer satisfaction and loyalty.
9. Resource Allocation
By having a structured marketing approach, you can allocate resources more effectively. This ensures that budgets, time, and manpower are allocated to the most impactful initiatives, maximizing the return on investment.
10. Innovation
While processes provide structure, they shouldn’t stifle creativity and innovation. Effective marketing process strike a balance between providing guidelines for consistent execution and allowing room for experimentation and innovative ideas.
In summary, methods in advertising and marketing are essential for developing a well-prepared, efficient, and effective approach to promoting your services or products. They allow your group to work cohesively, adapt to changes, and acquire measurable effects that make a contribution to the overall boom and success of your commercial enterprise.
Advantages of Processes
Processes in marketing offer numerous advantages that contribute to the overall success of a marketing strategy and the organization as a whole. Here are some specific advantages of implementing well-defined processes in marketing:
1. Consistency and Brand Identity
The marketing process ensures consistent messaging, branding, and design across all channels and touchpoints. This consistency helps reinforce brand identity, making it easier for customers to recognize and trust your brand.
2. Efficiency and Time Savings
Clear process streamline workflows, reduce bottlenecks, and eliminate unnecessary steps. This efficiency allows your marketing team to focus on strategic tasks and creative activities, leading to improved productivity and time savings.
3. Improved Collaboration
Processes outline roles, responsibilities, and communication channels within the marketing team and across other departments. This clarity enhances collaboration, reduces miscommunication, and ensures smoother cross-functional interactions.
4. Scalability
Well-defined process are essential for scaling marketing efforts as your business grows. New team members can quickly grasp the established procedures, ensuring consistent quality even during periods of expansion.
5. Measurable Results
Processes help set clear objectives, KPIs, and measurement methods for marketing campaigns. This enables accurate tracking of results, making it easier to assess the effectiveness of strategies and make data-driven decisions.
6. Adaptation to Change
Flexible processes can be adjusted to accommodate changes in the market, industry trends, and customer preferences. This adaptability ensures that your marketing remains relevant and responsive to evolving conditions.
7. Risk Management and Compliance
Documented processes promote adherence to industry regulations, ethical standards, and best practices. This minimizes the risk of legal issues, reputational damage, and other compliance-related challenges.
8. Enhanced Customer Experience
The marketing process that involve customer journey mapping ensure that every touchpoint aligns with the desired customer experience. This consistency leads to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
9. Resource Allocation
Defined processes facilitate better allocation of resources, such as budget, time, and manpower. Resources are allocated based on the most effective strategies and channels, maximizing ROI.
10. Innovation
While processes provide structure, they can also include avenues for testing new ideas and approaches. This balance between structure and innovation fosters creativity and helps your marketing stay ahead of the curve.
11. Knowledge Transfer and Onboarding
Documented processes make it easier to onboard new team members and transfer knowledge. New hires can quickly understand the established workflows, leading to faster integration into the team.
12. Consolidated Learning
When processes are documented, the lessons learned from previous campaigns and projects are captured. This knowledge can be shared within the team to avoid repeating mistakes and to build on successes.
13. Continuous Improvement
Processes provide a baseline for analysis and optimization. By regularly reviewing and refining processes, you can identify areas for improvement and ensure that your marketing strategies evolve.
In essence, the advantages of processes in marketing span improved efficiency, consistency, collaboration, adaptability, and the ability to drive measurable results. Well-designed processes contribute to a more effective and strategic approach to marketing, helping your organization achieve its marketing goals and maintain a competitive edge.
Disadvantages of Processes
While processes in marketing offer numerous advantages, they can also come with some disadvantages if not managed or implemented properly. Here are some potential disadvantages of marketing processes:
1. Rigidity
An overly rigid process can hinder creativity and innovation in marketing. If marketing teams are bound by strict guidelines, they may struggle to adapt to changing market trends or explore new and unconventional approaches.
2. Time-Consuming
An elaborate process may require significant time and resources to implement. This could delay marketing campaigns and reduce the organization’s ability to respond quickly to market opportunities.
3. Complexity
Complex process can be difficult to understand and follow, especially for new or inexperienced team members. This complexity may lead to confusion, errors, and reduced overall efficiency.
4. Resistance to Change
Implementing new marketing process might face resistance from existing team members who are accustomed to old practices. This resistance can impede the adoption of more efficient or effective process.
5. Overemphasis on Metrics
While metrics are essential for measuring marketing performance, excessive focus on specific metrics can lead to tunnel vision. It may overlook the qualitative aspects of marketing efforts and fail to capture the full customer experience.
6. One-Size-Fits-All Approach
Standardized strategies might not cater to the particular desires and traits of various marketplace segments or products. Applying a one-size-fits-all approach might also result in less personalized advertising and marketing techniques.
7. Lack of Flexibility
In some cases, the shape imposed via process can avoid adaptability. Marketing teams may struggle to respond to unexpected opportunities or challenges outside the predefined process boundaries.
8. Increased Bureaucracy
Complex process can introduce unnecessary bureaucracy, with excessive paperwork, approvals, and sign-offs. This bureaucratic burden may slow down decision-making and impede creativity.
9. Risk of Becoming Stale
Following the same process repeatedly may lead to marketing campaigns that feel stale or lacking in innovation. This could result in decreased customer engagement and interest over time.
10. Disconnect from Real-Time Data
A rigid process may not allow marketing teams to react quickly to real-time data and customer feedback. As a result, opportunities to capitalize on emerging trends or address immediate issues might be missed.
11. Neglecting Human Judgment
Overreliance on process may devalue the role of human judgment and experience in decision-making. This can lead to missed opportunities for creative solutions and strategic thinking.
To address these potential disadvantages, businesses should strike a balance between having structured processes and fostering a culture of adaptability and innovation. Regularly evaluating and refining processes, encouraging feedback from marketing teams, and being open to experimentation can help mitigate these disadvantages and maximize the benefits of marketing processes.
Conclusion
The marketing process are the backbone of any successful marketing strategy, serving as a structured roadmap to guide organizations from ideation to execution. By understanding and implementing the key stages of marketing processes—research, planning, implementation, and evaluation—businesses can enhance efficiency, ensure consistency, and achieve their goals effectively.
In today’s competitive landscape, marketing is no longer just about creating compelling messages; it’s about creating value-driven, customer-centric campaigns that resonate. The process of marketing enables businesses to identify customer needs, craft personalized solutions, and measure success through data-driven insights.
A thorough understanding of marketing processes ensures that organizations stay agile, adapt to changing market dynamics, and maintain alignment between their goals and customer expectations. Whether you’re a marketer, entrepreneur, or student, mastering these processes empowers you to make informed decisions and build impactful campaigns.
Ultimately, embracing a well-defined marketing process leads to better resource allocation, stronger customer relationships, and sustained business growth.



