Introduction to Process in Marketing
The marketing process is the backbone of effective marketing strategies. It provides a structured approach to identifying opportunities, engaging customers, and achieving business goals. These processes act as a roadmap, guiding businesses from the initial stages of market research to the final campaign performance evaluation.
At its core, the marketing process begins with market research—a critical step to understanding customer needs, preferences, and market trends. This research lays the foundation for crafting targeted strategies that resonate with the intended audience.
The next step involves strategy development, where businesses define their objectives, target audience, and value proposition. This phase ensures that all marketing efforts are aligned with the organization’s overall goals, creating a clear focus and direction.
Once the strategy is in place, the process moves to implementation. This is where the planning turns into action through advertising, promotions, and other marketing campaigns. A successful implementation requires creativity, collaboration, and effective use of resources.
Finally, monitoring and evaluation close the loop by analyzing the performance of marketing efforts. Businesses rely on metrics like customer engagement, sales growth, and return on investment (ROI) to assess success and identify areas for improvement.
The importance of marketing processes lies in their ability to bring structure and consistency to marketing activities. They help businesses allocate resources wisely, maintain brand integrity, and adapt to changing market dynamics. In today’s competitive environment, understanding and implementing these processes is essential for businesses to remain relevant and achieve sustainable growth. By following a systematic marketing strategy, organizations can create value-driven campaigns that foster strong customer relationships and drive long-term success. Whether new to marketing or a seasoned professional, mastering these strategies is key to thriving in the ever-evolving marketplace.

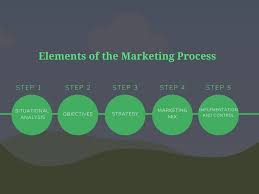
Key Elements of Marketing Process
Marketing processes are systematic approaches that businesses use to connect with their target audience, deliver value, and achieve their goals. It provides a structured framework for identifying opportunities, creating impactful strategies, and implementing effective campaigns. The key elements of the marketing processes ensure that every step is aligned, customer-focused, and results-oriented. Here are the essential components:
1. Market Research
Market research is the cornerstone of the marketing processes. It involves gathering data about the target audience, competitors, industry trends, and market conditions. By analyzing this information, businesses gain a deep understanding of customer preferences, pain points, and purchasing behaviors. This insight helps in identifying opportunities and making informed decisions about product development, pricing, and promotion strategies. Market research also reduces risks by ensuring that marketing efforts are grounded in real-world data rather than assumptions.
2. Strategy Development
Once the research phase is complete, businesses move on to strategy development. This involves defining the organization’s marketing objectives, identifying the target audience, and crafting a compelling value proposition. A well-thought-out strategy provides direction for all marketing activities, ensuring they are focused on achieving specific goals. It also helps in differentiating the product or service from competitors by highlighting its unique benefits.
3. Implementation
In this phase, the marketing strategy comes to life. Implementation involves executing marketing campaigns, promotions, and other activities designed to reach the target audience. It includes selecting the right marketing channels, creating engaging content, and launching initiatives such as social media campaigns, email marketing, and traditional advertising. Effective implementation requires coordination among teams, adherence to timelines, and efficient use of resources.
4. Monitoring and Evaluation
The final element of the marketing processes is monitoring and evaluation. This step focuses on measuring the performance of marketing activities to determine their success. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer engagement, sales, brand awareness, and return on investment (ROI) are tracked to assess outcomes. By analyzing these metrics, businesses can identify what worked, what didn’t, and how to improve future campaigns. Continuous evaluation ensures that marketing efforts remain dynamic and adaptable to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, the marketing processes are not just about reaching customers; it’s about building relationships, delivering value, and driving long-term success. Understanding and implementing these key elements can help businesses navigate competitive markets and create impactful, results-driven strategies. Whether you’re a startup or a large corporation, mastering the marketing strategy is essential for sustained growth and relevance.
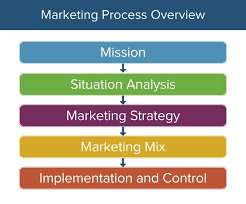
Types of Process
Within the realm of marketing, a multitude of processes unfold across various stages, encompassing planning, execution, and analysis. Below are the prevalent types of processes in marketing:
1. Market Research Process
This involves gathering, scrutinizing, and interpreting data about the target market, clientele, and competitors. It encompasses surveys, interviews, focus groups, and the analysis of secondary data to glean insights into customer inclinations, necessities, and market trends.
2. Segmentation Process
This entails partitioning the market into distinct clusters based on shared attributes, conduct, and preferences. Segmentation empowers businesses to target specific customer segments with tailored marketing approaches.
3. Product Development Process
This encompasses ideation, design, testing, and launch of novel products or enhancements to existing ones. It entails market research, idea generation, product testing, and commercialization.
4. Branding and Positioning Process
Here, a unique brand identity is crafted and positioned within customer perception. This encompasses delineating the brand’s personality, values, and differentiators to carve a competitive edge.
5. Promotion Process
This focuses on propagating products or services to the intended audience. It comprises advertising, public relations, sales promotions, direct marketing, and other promotional undertakings to heighten awareness and evoke interest.
6. Digital Marketing Process
This harnesses digital platforms to engage the target audience. It includes online advertising, social media marketing, email campaigns, content propagation, and search engine optimization (SEO).
7. Sales Process
This involves transitioning leads into paying patrons. It encompasses lead generation, nurturing, sales presentations, negotiation, and finalizing deals.
8. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Process
Here, interactions with customers across their lifecycles are managed. This encompasses capturing customer data, dissecting behavioral trends, and leveraging insights to personalize communication and bolster satisfaction.
9. Distribution and Channel Management Process
This steers product or service conveyance from manufacturers to end consumers. It entails selecting and overseeing distribution channels such as wholesalers, retailers, and digital platforms.
10. Marketing Analytics Process
This entails collating, analyzing, and interpreting data pertinent to marketing efficacy. Such analytics facilitate the measurement of marketing impact and offer insights for data-driven decisions.
11. Content Creation Process
This concerns the formulation of valuable content for marketing objectives. It involves ideation, creation, editing, and dissemination through assorted channels.
12. Lead Generation Process
This entails kindling and capturing potential customer’s interest in products or services. Activities include content propagation, social media engagement, and online lead capture forms.
These examples merely scratch the surface of marketing processes. The specific processes embraced by businesses might differ contingent on their goals, industry, target demographic, and overarching marketing strategy. The implementation of effective processes can streamline marketing initiatives, elevate customer interaction, and propel business expansion.
Some Concepts Related to Process
Several concepts are related to processes, particularly in the context of marketing and business operations. Understanding these concepts is essential for optimizing processes and achieving desired outcomes. Here are some key concepts related to processes:
1. Process Mapping
Process mapping is a visible illustration of a manner that shows the series of sports, decisions, and interactions concerned with accomplishing a specific goal. It facilitates identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and opportunities for development in the processes.
2. Workflow
A workflow is a series of interconnected steps or responsibilities that want to be finished to accomplish a specific goal. Workflows define the sequence of moves, obligations, and dependencies among distinctive degrees of a process.
3. Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is the ongoing effort to enhance processes and practices incrementally. It involves figuring out areas for development, enforcing adjustments, and frequently comparing consequences to make iterative refinements.
4. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
SOPs are written files that define step-by-step commands for carrying out precise tactics. They offer a standardized and consistent method for finishing tasks and make sure that pleasant practices are followed.
5. Process Automation
Process automation involves the use of generation and software to automate repetitive duties or movements inside a procedure. Automation can enhance efficiency, reduce human blunders, and free up sources for extra strategic sports.
6. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
KPIs are measurable metrics used to measure the overall performance and effectiveness of a procedure. They provide quantitative data to evaluate whether the process is meeting its objectives and can indicate areas that require attention or improvement.
7. Lean Six Sigma
Lean Six Sigma is a management methodology that combines Lean principles (aimed at eliminating waste and optimizing processes) with Six Sigma (focused on reducing defects and variations). It aims to achieve higher process efficiency and quality.
8. Root Cause Analysis
Root cause analysis is a problem-solving technique used to identify the underlying reasons for issues or challenges in a process. By addressing root causes, businesses can prevent recurring problems and improve process performance.
9. Business Process Reengineering (BPR)
BPR is the radical redesign of business processes to achieve significant improvements in performance, efficiency, and customer satisfaction. It involves questioning and challenging existing processes to introduce innovative changes.
10. Process Performance Metrics
Process performance metrics measure the effectiveness, efficiency, and quality of a process. These metrics help monitor process performance and identify areas for improvement.
11. Value Stream Mapping
Value stream mapping is a lean technique that visually represents the flow of materials, information, and actions in a process. It helps identify areas of waste and opportunities to add value to the process.
By applying these concepts, businesses can optimize their strategies, streamline operations, and achieve better outcomes, ultimately leading to improved customer satisfaction, increased productivity, and higher levels of success.
Process for Marketing Strategy
Processes within a marketing strategy denote the methodical and organized approach adopted by businesses to devise, implement, and assess their marketing endeavors. This entails the formulation and execution of well-structured strategies that guide diverse marketing activities, steering them towards specific objectives and goals. The integration of processes into a marketing strategy unfolds as follows:
1. Market Research Process
The foundation of a marketing strategy rests upon comprehensive market research to fathom the target audience, their desires, inclinations, and conduct. This investigative strategy encompasses data aggregation from diverse sources, its analysis, and the utilization of insights to shape the overarching marketing strategy.
2. Segmentation and Targeting Process
Following the market research phase, businesses segment the market based on shared attributes and needs. This step identifies the most suitable target audience for their offerings. By discerning the target demographic, businesses tailor their marketing messages and positioning to resonate with the intended consumers.
3. Branding and Positioning Process
A well-crafted marketing strategy features a well-defined branding and positioning process. Here, a unique brand identity, personality, and positioning are sculpted to distinguish the enterprise from competitors and forge a distinctive market presence.
4. Promotion Process
The marketing strategy delineates the promotion process, encompassing the selection of appropriate marketing channels, messaging, and communication tactics. Businesses determine the most effective avenues to engage their target audience, fostering awareness, kindling interest, and driving conversions.
5. Digital Marketing Process
In the digital era, digital marketing stands as a cornerstone of marketing strategies. The strategy incorporates a digital marketing process that maps out the utilization of various online platforms such as social media, email, content marketing, and search engine optimization to effectively engage the target demographic.
6. Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Process
Marketing strategies also embrace the sales process and customer relationship management. This entails defining the sales funnel, lead generation, and nurturing, as well as strategies to cultivate enduring customer relationships and loyalty.
7. Measurement and Analytics Process
A pivotal facet of marketing strategy revolves around measurement and analytics. Businesses establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics to monitor the efficacy of marketing activities. By dissecting data and performance metrics, they can make informed decisions and optimize marketing endeavors.
8. Ongoing Enhancement
Marketing strategies underscore perpetual refinement, where businesses regularly assess and enhance their marketing processes grounded in feedback and performance evaluations. This iterative approach empowers them to adapt to shifting market dynamics and evolving customer preferences.
9. Alignment with Business Objectives
Marketing strategies dovetail with overarching business objectives. The processes are meticulously designed to buttress the attainment of broader organizational aims, be it augmenting revenue, expanding market share, or heightening brand recognition.
By assimilating processes into a marketing strategy, businesses can attain enhanced synchronization, efficiency, and uniformity in their marketing undertakings. These strategies ensure methodical planning, data-driven methodologies, and alignment with the target audience’s demands, ultimately culminating in more fruitful marketing campaigns and favorable business outcomes.

Steps in the Marketing Process
The marketing process is a series of structured steps that guide businesses in creating, delivering, and communicating value to their customers. Each step is designed to ensure that marketing efforts are effective, customer-focused, and aligned with organizational goals. Below are the key steps involved in the marketing process:
1. Understanding the Market and Customer Needs
- Conduct market research to gather insights about customer needs, preferences, and pain points.
- Analyze market trends, competitive landscape, and economic factors to identify opportunities.
- Develop a clear understanding of the target audience’s behavior and expectations.
2. Defining the Marketing Strategy
- Segmentation: Divide the market into distinct customer groups based on shared characteristics.
- Targeting: Select the most promising segments to focus marketing efforts on.
- Positioning: Create a unique and compelling value proposition that differentiates the product or service from competitors.
- Establish clear marketing objectives aligned with business goals.
3. Developing the Marketing Mix (4Ps/7Ps)
- Product: Design or refine the product/service to meet customer needs.
- Price: Determine a pricing strategy that reflects value while being competitive.
- Place: Choose distribution channels to ensure the product is easily accessible to the target audience.
- Promotion: Plan communication strategies, including advertising, public relations, and digital marketing.
For service-oriented businesses, additional Ps include: - People: Train and empower staff to enhance customer experience.
- Process: Streamline workflows for delivering products/services efficiently.
- Physical Evidence: Ensure tangible elements (e.g., branding, environment) reinforce the offering’s quality.
4. Implementation and Execution
- Launch marketing campaigns, promotions, and initiatives across selected channels.
- Coordinate efforts among teams to ensure seamless execution of strategies.
- Monitor the timeline, budget, and resource allocation to keep activities on track.
5. Monitoring and Evaluation
- Track the performance of marketing activities using key performance indicators (KPIs) such as customer engagement, sales growth, and ROI.
- Use analytics tools and customer feedback to assess what is working and what needs adjustment.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of strategies to inform future decisions and refine the approach.
6. Building and Nurturing Customer Relationships
- Focus on long-term engagement by providing exceptional customer service and value.
- Use customer relationship management (CRM) tools to manage and personalize interactions.
- Foster loyalty through programs, incentives, and consistent communication.
The marketing process is a dynamic and iterative cycle that requires constant learning and adaptation. By following these steps, businesses can create value-driven marketing strategies that resonate with their target audience, achieve their objectives, and build lasting customer relationships.
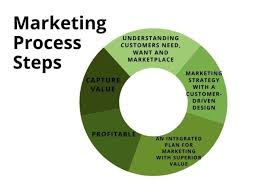
Conclusion: Processes in Marketing
The marketing process is a vital framework that guides businesses in navigating the complexities of today’s competitive marketplace. By understanding and implementing the core elements of the marketing process—market research, strategy development, implementation, and evaluation—organizations can create more targeted, effective, and sustainable marketing strategies.
A structured marketing approach ensures that every action, from understanding customer needs to delivering value, is intentional and aligned with business objectives. Market research provides the foundation, offering insights into customer preferences and market dynamics. Strategy development then translates this knowledge into actionable plans, ensuring that campaigns and initiatives are well-focused and goal-oriented.
Implementation is where ideas and plans take shape, requiring creativity, collaboration, and precise execution. However, the process does not end with execution. Monitoring and evaluation are critical to assess performance, measure results, and refine strategies for better outcomes. This continuous feedback loop ensures that businesses can adapt to changing customer behaviors and market trends, keeping their marketing efforts relevant and impactful.
The importance of the marketing process extends beyond achieving immediate goals. It fosters a customer-centric approach, enhances efficiency, and promotes consistency across all marketing channels. Moreover, it empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimize resources, and maintain a competitive edge in the dynamic world of marketing.
In conclusion, introducing and mastering processes in marketing is essential for businesses aiming to thrive in today’s fast-paced environment. Whether you are launching a new product, building brand awareness, or expanding into new markets, a well-defined marketing process serves as the roadmap to success. By integrating these processes into your marketing strategy, you can ensure long-term growth, customer satisfaction, and sustained business performance.