Introduction to the 8Ps of Marketing
Welcome to the world of advertising! As businesses strive to connect with their customers and develop successful marketing strategies, the traditional 4Ps of marketing—product, price, place, and promotion—serve as the foundation. However, as the business landscape evolves and becomes more consumer-centric, an expanded framework known as the 8Ps of marketing has emerged. This new approach addresses a broader range of factors to meet the demands of the modern marketplace.
The 8Ps of marketing add depth and dimension to the conventional marketing mix, highlighting the importance of understanding and engaging with customers throughout the marketing process. Let’s take a closer look at each of the 8Ps:

1. Product
In marketing, a product is a tangible good, service, or idea businesses or companies present to meet consumer needs or desires. It is one of the middle factors of the advertising mix, which also includes rate, place (distribution), and advertising. A nicely defined and strategically located product is critical for an organization’s success in the marketplace.
Here are some key aspects of a product’s advertising and marketing:
1. Types of Products
Products may be categorized into different sorts, along with patron goods (products purchased for non-public use), business goods (products utilized by companies for manufacturing), services (intangible services like banking, healthcare, or consulting), and thoughts (inclusive of social or public health campaigns).
2. Product Attributes
Product attributes refer to the traits and features that outline the product. These attributes can encompass physical traits, price, design, packaging, brand call, and warranties.
3. Product Life Cycle
Products commonly go through a lifestyle cycle that includes four ranges: creation, increase, adulthood, and decline. Understanding the product existence cycle enables entrepreneurs to tailor their techniques at each stage.
4. Product Differentiation
Product differentiation entails distinguishing a product from its competition by showcasing distinct capabilities, advantages, or traits. It allows for a competitive gain and fosters logo loyalty.
5. Branding
Branding is the process of creating a unique identity and photo for a product through the use of an awesome logo, name, brand, and design. A sturdy emblem can affect client perceptions and loyalty.
6. Product Positioning
Product positioning refers to how a product is perceived and located within the minds of customers relative to competitors. Effective positioning allows agencies to target unique client segments and address their wishes.
7. Product Mix
The product mix, instead called the product portfolio, encompasses the whole range of products furnished through an enterprise. It can encompass several products catering to one-of-a-kind markets and consumer segments.

8. Product Development
Product improvement includes the process of creating new merchandise or editing current ones to satisfy changing purchaser demands and marketplace tendencies.
9. Product Packaging
Packaging performs a vital role in product advertising and marketing because it not only protects the product but also communicates logo identity and impacts purchasing decisions.
10. Product Distribution
Product distribution is about making the product to be delivered to clients through various channels, which include retail shops, online platforms, wholesalers, or direct income.
11. Product Adoption
Product adoption refers back to how customers end up privy to a product, strive for it, and decide to apply it often. Marketers focus on facilitating product adoption to drive sales and purchaser loyalty.
12. Product Recall and After-Sales Service
In cases of product defects or troubles, businesses may need to conduct product recalls to ensure client safety. Additionally, providing first-rate after-sales service helps construct, consider, and maintain consumer delight.
13. Cross-Selling and Upselling
Successful products can facilitate pass-promoting and upselling possibilities, where customers are encouraged to buy additional merchandise or premium variations.
14. Long-Term Success
Companies with a strong product portfolio and a focus on non-stop improvement are more likely to gain long-term period success and sustainability within the marketplace.
In the end, the product is in the middle of advertising efforts, and its significance lies in its capacity to satisfy customer needs, differentiate the business enterprise from competitors, construct logo equity, and force revenue and growth. Understanding the significance of the product allows businesses to increase powerful advertising and marketing strategies that result in consumer pleasure, multiplied marketplace proportion, and common enterprise achievement.

2. Price
Price is one of the foundational elements of the marketing blend, along with product, place, and promotion. It is a critical component that directly impacts purchaser behavior and determines the revenue generated by a commercial enterprise. In advertising, price refers to the amount of price customers are willing to pay in exchange for a service or product presented by a business enterprise.
The price of a product or service is not just an easy quantity; it carries sizeable implications for a business enterprise’s profitability, brand perception, and market positioning. Finding the right pricing approach is a sensitive matter because it must align with both customer expectations and the business enterprise’s financial goals.

A powerful pricing approach considers various factors, including the price of manufacturing, competitor pricing, market demand, and the perceived fee to customers. Depending on the advertising goals and target marketplace, companies can also adopt exceptional pricing methods, including penetration pricing, skimming pricing, price-based pricing, and aggressive pricing.
Price plays a critical role in shaping customer perceptions. A better rate may also signal top-rated high-quality or exclusivity, while a lower rate might be associated with affordability or price effectiveness. Striking the proper balance between perceived fee and rate is important in attracting and retaining customers, as well as staying aggressive in the market.
In the end, price is a critical factor in the marketing mix that directly influences an enterprise’s revenue and brand positioning. Finding the most advantageous pricing strategy calls for a deep know-how of the target market, competitive landscape, and purchaser choices. By placing the proper pricing, businesses can efficiently meet consumer needs, reap their economic targets, and hold an aggressive position in the market.

3. Place
In marketing, a “place” refers to one of the fundamental components of the marketing mix, often referred to as the “4Ps.” The other three Ps are product, price, and promotion. Place, additionally called distribution, is the specialty of how an employer’s services or products are made available to the target customers.
The idea of region includes the strategic selections and actions taken by corporations to make certain that their services reach the right customers at the right time and within the proper area. It’s all about growing a clean and efficient channel through which products can flow from the manufacturer to the end-user or customer.
Here are a few key factors and considerations related to the “area” aspect of advertising and marketing:
1. Distribution Channels
Businesses want to determine the most suitable distribution channels to deliver their products or services. These channels may want to include direct income, wholesalers, shops, distributors, online marketplaces, and more. The preference for distribution channels depends on elements like the nature of the product, the target marketplace, and the organization’s basic advertising approach.
2. Market Coverage
Companies have to determine the quantity of their marketplace insurance, which can be categorized as intensive, selective, or unique distribution. Intensive distribution involves placing products in as many outlets as possible to achieve widespread availability. Selective distribution involves choosing specific retail outlets or partners that align with the brand image and target market. Exclusive distribution, then again, restricts the availability of the product to just a few carefully decided-upon shops, creating an air of mystery about exclusivity.
3. Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is crucial in the distribution process. Businesses need to strike a balance between retaining sufficient stock to meet customer demand while minimizing holding expenses and the danger of inventory obsolescence.
4. Transportation and Logistics
An effective transportation and logistics machine is vital for ensuring that products reach their locations right away and in their true situation. This aspect becomes even more critical in cases of international distribution.

5. Physical Presence
In addition to considering online distribution methods, businesses must also think about their physical presence in the market. This includes deciding on the number and location of retail stores, warehouses, and other facilities.
6. Customer Convenience
Convenience is a large component in the fulfillment of distribution techniques. Companies want to make their products effortlessly reachable to clients, both through physical places and convenient online systems.
7. Channel Relationships
Managing relationships with intermediaries like retailers and distributors is vital. Businesses must build and maintain strong partnerships with these channel members to ensure their products receive proper attention and promotion.
8. E-commerce and Digital Distribution
With the upward push of e-trade and virtual structures, organizations need to evolve their distribution strategies to incorporate online sales channels efficiently.
The effectiveness of an area strategy can extensively impact a business enterprise’s achievement in the marketplace. By making sure products are available where and when customers want them, organizations can enhance customer satisfaction and gain a competitive advantage.
4. Promotion
Promotion is one of the vital additives of the advertising blend, which also consists of product, price, and place (distribution). It is a set of advertising and marketing strategies geared toward communicating the value of a service or product to the target market and persuading them to make a purchase or take a particular action. Effective promotion is crucial for growing cognizance, generating interest, and, in the long run, riding income.
Promotion refers back to the various strategies and tools utilized by groups and entrepreneurs to promote their products or services and entice potential customers. The number one intention of the promotion is to communicate the particular selling propositions, advantages, and benefits of a product or service to the target marketplace, ultimately influencing customer behavior in choosing of the promoted offering.

Promotion encompasses several activities, such as advertising, public family members, sales promotions, private selling, and direct advertising. These promotional methods can, in my opinion, be used in aggregate to create a comprehensive advertising and marketing campaign.
1. Advertising
Advertising involves paid and non-personal communication through numerous media channels, including TV, radio, print (newspapers, magazines), online platforms (websites, social media), and outdoor shows (billboards, posters). The purpose of marketing is to reach a large target audience and construct brand recognition, encouraging potential customers to not forget the products or services.
2. Public Relations (PR)
PR specializes in managing the public perception of a brand or business enterprise. It includes sports, which include press releases, media interviews, occasions, sponsorships, and community involvement to construct an advantageous picture and maintain a terrific relationship with the public.
3. Sales Promotions
Sales promotions are short-term period incentives aimed at stimulating instant buying behavior. Examples include discounts, coupons, unfastened samples, contests, and confined-time offers. These promotions create a sense of urgency, encouraging customers to make a purchase quickly.
4. Personal Selling
Personal selling is a one-on-one communication method in which sales representatives interact without delay with capable customers. This method allows for custom-designed presentations and responses to purchaser issues, making it effective for excessive-involvement services or products.
5. Direct Marketing
Direct advertising entails achieving out-of-capacity customers without delay, bypassing intermediaries. It consists of electronic mail advertising, direct mail, telemarketing, and other personalized conversation strategies. Direct marketing is particularly powerful in attaining precise goal segments.
Effective promotion requires carefully making plans, informing the target audience, and aligning the promotional techniques with standard marketing objectives. By employing the right blend of promotional sports, agencies can attract brand attention, create hobbies, and, in the end, increase income and business.

5. People
In the realm of business, marketing stands as a pivotal facet, requiring a collaborative effort from diverse professionals to effectively propel products, services, or brands toward intended audiences. These individuals hold pivotal roles in devising and executing successful marketing strategies that stimulate sales, enhance brand recognition, and foster engagement with customers. Let’s delve into the pivotal roles and responsibilities undertaken by these marketing stalwarts:
1. Marketing Manager
The marketing manager shoulders the responsibility of supervising the entire marketing team and formulating comprehensive marketing strategies. They analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and competitive landscapes to develop campaigns aligned with the company’s objectives. Marketing managers also allocate budgets, set goals, and assess the efficacy of marketing endeavors.
2. Brand Manager
Brand managers are dedicated to establishing and preserving a robust brand image for a company or product. They focus on brand positioning, messaging, and imaginative campaigns tailored to resonate with the target audience. Brand managers often collaborate with marketing teams to ensure a consistent brand portrayal across all marketing platforms.
3. Digital Marketer
Digital marketers harness online platforms and technologies to endorse products or services. They orchestrate digital marketing campaigns, encompassing activities like email marketing, social media engagement, search engine optimization (SEO), pay-per-click (PPC) advertising, and content marketing.
4. Content Marketer
Content marketers shoulder the task of curating valuable and pertinent content that captivates and engrosses the target audience. They craft blog posts, articles, videos, infographics, and various content formats to boost traffic, establish expertise, and ultimately transform potential leads into customers.
5. Social Media Manager
Social media managers oversee a company’s presence across diverse social media platforms. They forge social media strategies, generate and curate content, interact with followers, and monitor social media metrics to optimize performance.

6. Marketing Analyst
Marketing analysts harness data and analytics tools to assess the efficiency of marketing campaigns. They track key performance indicators (KPIs) to gauge return on investment (ROI) and offer insights to refine forthcoming marketing endeavors.
7. Public Relations (PR) Specialist
PR specialists steer the public image and standing of a company or brand. They manage interactions with media, draft press releases, and navigate crisis communications to uphold a favorable public perception.
8. Market Researcher
Market researchers conduct studies and collate data to comprehend consumer preferences, behaviors, and market trends. This intelligence shapes marketing strategies and informs product development.
9. Advertising Manager
Advertising managers oversee the creation and execution of advertising campaigns. They collaborate with creative teams, copywriters, and media planners to roll out compelling advertisements that resonate with the intended audience.
10. Sales and Marketing Coordinator
Sales and marketing coordinators serve as a bridge between marketing and sales teams. They facilitate the coordination of promotional activities, oversee lead generation, and ensure seamless communication between departments.
These roles often exhibit interplay, particularly in smaller organizations, and effective teamwork is pivotal for the fruition of prosperous marketing campaigns. Given the swift evolution within the marketing sphere, these professionals must remain attuned to the latest trends, tools, and technologies, ensuring their ability to stay competitive and deliver substantial outcomes for their enterprises.

6. Processes
Marketing is an essential component of any commercial enterprise that seeks to create, talk, deliver, and alternate prices to its clients. It involves diverse methods designed to identify, appeal to, and keep customers while at the same time attaining the company’s dreams. These processes are crucial for businesses to understand their target audience, build strong relationships, and drive revenue.
Here are some key processes in marketing:
1. Market Research
Market studies are the muse of all marketing sports. It entails accumulating and reading the target market’s records, including customer wishes, preferences, behaviors, and competitors. By gaining expertise in the market, groups can make knowledgeable selections and broaden effective advertising techniques. Businesses can make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies by understanding the market.
2. Segmentation and Targeting
Once the market studies are carried out, the next step is to section the market based totally on factors such as demographics, psychographics, and conduct. This process allows businesses to divide the market into distinct groups with similar characteristics. After segmentation, the enterprise identifies its target marketplace, and the precise institution(s) it aims to serve with its products or services.
3. Product/Service Development
The technique of making or improving products and services that meet the needs and alternatives of the target market. It includes designing, checking out, and refining the services to make certain they provide value and cope with customer pain factors.
4. Branding and Positioning
Branding is the technique of making a unique and recognizable identification for the business or its products or offerings. Positioning, then again, entails organizing a specific area inside the minds of the customers relative to the competition. Effective branding and positioning help build customer loyalty and preference.
5. Promotion and Advertising
Promotion is the verbal exchange of the services or product’s blessings and capabilities with the target market. Advertising is one of the most commonplace promotion strategies, involving the use of various channels such as TV, radio, print, virtual, and social media. Other promotional activities encompass public relations, sales promotions, and direct advertising and marketing.
6. Distribution and Channel Management
Distribution refers to the technique of turning in services or products from the producer to the give-up customer. Channel management entails selecting and managing the maximum number of green distribution channels, inclusive of wholesalers, retailers, and online platforms, to reach the target market effectively.
7. Sales and Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Sales are the process of converting leads into paying customers. An efficient sales process involves prospecting, lead qualification, pitching, negotiating, and closing the sale. CRM encompasses managing interactions with customers throughout their lifecycle to foster long-term relationships and repeat business.
8. Digital Marketing and Analytics
In the digital age, online marketing performs a big function. Digital advertising and marketing encompass numerous channels, along with websites, social media, electronic mail, engines like Google, and content advertising. Analytics equipment is used to track and measure advertising performance, presenting valuable insights to optimize strategies.
9. Evaluation and Improvement
Continuous evaluation of marketing efforts is essential to gauge the effectiveness of various activities. Metrics consisting of return on investments (ROI), customer satisfaction, and purchaser retention prices help groups discover areas for development and refine their advertising processes.
In conclusion, marketing procedures are essential for companies to apprehend their target marketplace, expand products and offerings that meet consumer wishes, and effectively promote and distribute them to achieve business goals. By following nicely defined methods, companies can construct robust brand focus, and consumer loyalty, and ultimately drive boom and success.

7. Positioning
Positioning is an essential concept in advertising that plays an essential role in defining how a product, brand, or corporation is perceived by its target audience about its competition. It is the art and technological know-how of creating a wonderful and valuable place in the minds of customers and positioning your offering in a way that sets it apart and addresses the specific needs and desires of your target marketplace section.
The concept of positioning became popularized through Al Ries and Jack Trout in their influential 1981 book “Positioning: The Battle for Your Mind.” They argued that during a brand-new crowded marketplace in which purchasers are bombarded with data and selections, it is crucial to create a clean, memorable, and applicable image for your product or brand.
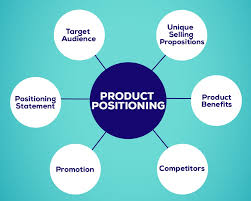
Effective positioning involves several key elements:
1. Identifying Your Target Audience
You want a deep understanding of your perfect customers. Who are they? What are their choices, desires, and pain points? This knowledge helps you tailor your positioning to resonate with them.
2. Differentiation
What sets your product or brand apart from the competition? It could be unique features, benefits, values, or even a specific niche you’re serving. Differentiation creates a reason for consumers to choose you over alternatives.
3. Value Proposition
Your positioning should communicate the value you provide. This goes beyond just listing features; it’s about addressing the specific problems or aspirations your target audience has.
4. Consistency
Positioning must be consistent across all touchpoints, from your advertising and website to your customer service and product experience. Inconsistencies can confuse and weaken your positioning.
5. Relevance
Your positioning needs to be relevant to your target market. It should align with their interests and desires, addressing what matters most to them.
6. Sustainability
Positioning isn’t a short-term tactic. It’s a strategic approach that should guide your overall marketing efforts. As the marketplace evolves, you may need to modify your positioning to remain relevant.
7. Perception Management
While you may influence how you position yourself, it is vital to take into account how your target audience certainly perceives you. Monitoring and managing this perception over time is crucial.
Remember, effective positioning facilitates creating a mental space inside the customer’s mind, making it easier for them to remember you, understand your unique value, and, in the end, choose your product or brand over the competition. It’s an effective tool within the marketer’s toolkit for constructing a robust and lasting connection with customers.
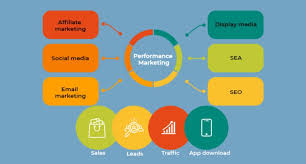
8. Performance
Performance in advertising refers back to the measurement, assessment, and optimization of various marketing sports to attain unique goals and pressure-favored effects. It is an essential factor of modern-day marketing that enables groups to assess the effectiveness of their strategies, approaches, and campaigns, ultimately leading to stepped-forward decision-making, better resource allocation, and extended return on investment (ROI).
The performance aspect of advertising is essential, as it affords precious insights into what’s operating and what needs adjustment. By analyzing performance metrics and key performance indicators (KPIs), entrepreneurs can decide which channels, messages, and processes resonate with their target audience, leading to superior customer engagement and conversion.
In the brand-new statistics-driven landscape, performance advertising and marketing have become cornerstones of successful advertising and marketing strategies. Whether -it’s measuring the effect of virtual advertising, monitoring website conversions, evaluating the effectiveness of social media campaigns, or analyzing the ROI of content material marketing efforts, overall performance measurement provides a stable basis for making knowledgeable marketing decisions.

Key elements of performance in marketing include:
1. Setting Clear Objectives
Defining specific, measurable goals is essential for assessing performance. Whether it is increasing sales, improving brand awareness, generating leads, or enhancing customer loyalty, clear objectives provide a benchmark for success.
2. Data Collection and Analysis
Gathering relevant data from various marketing activities and channels is critical. Robust analytics tools and data analysis techniques allow marketers to gain insights into customer behavior, campaign effectiveness, and overall performance.
3. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Identifying the right KPIs helps measure progress toward objectives. KPIs can include metrics such as conversion rates, customer acquisition costs, click-through rates, customer lifetime value, and more.
4. A/B Testing and Experimentation
Testing different approaches (A/B testing) helps marketers refine strategies by comparing performance. Experimentation allows for continuous optimization to achieve better results.
5. Optimization and Iteration
Based on performance analysis, marketers can refine their tactics and strategies. Iterative optimization ensures that marketing efforts become increasingly effective over time.
6. Budget Allocation
Performance data helps allocate marketing budgets more effectively by focusing resources on channels and strategies that deliver the best results.
7. ROI Assessment
Calculating the return on investment for marketing initiatives helps demonstrate the value generated from the resources invested in these activities.
By emphasizing performance measurement and optimization, businesses can stay agile, responsive to market changes, and deliver better experiences to their target audience, ultimately leading to a more competitive and successful marketing strategy.




Nice Information.
Thank you so much
Hey, I’m Jack. Your blog is a game-changer! The content is insightful, well-researched, and always relevant. Great job!
Thanks Jack